What Is Cervidil—and How Does It Help Induce Labor?
In a perfect scenario, baby would arrive when the moment is just right for you and your family. But, in reality, babies come on their own timeline—and if your little one is on the late side (or you have a high-risk pregnancy), your doctor might recommend something to help jump-start labor.
That’s where a medication like Cervidil comes into play: It can help your cervix dilate (open up) and efface (thin out) in preparation for labor. But what is Cervidil, exactly, and are there potential risks when using Cervidil for induction? Here’s what you need to know.
Cervidil is the brand name for dinoprostone, a medication that’s used to help induce labor, says Alexa Sassin, MD, an assistant professor in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. “It’s a vaginal insert that contains dinoprostone, which is similar to natural prostaglandins found in the body,” she explains. Prostaglandins like dinoprostone help prepare the cervix for labor and delivery by softening it in a process known as “cervical ripening,” Sassin says.
“It’s necessary for the cervix to soften, so that the cervix can dilate completely and allow for the delivery of baby,” she says.
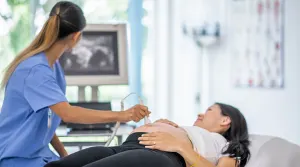
Cervidil is inserted into your vagina by a healthcare professional, explains Meleen Chuang, MD, a clinical associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine and medical director at the NYU Langone Family Health Center. “For the first two hours following insertion, you should remain lying down,” she says. “If you sit up or walk after the first two hours, you should be careful to ensure the insert remains in place.”
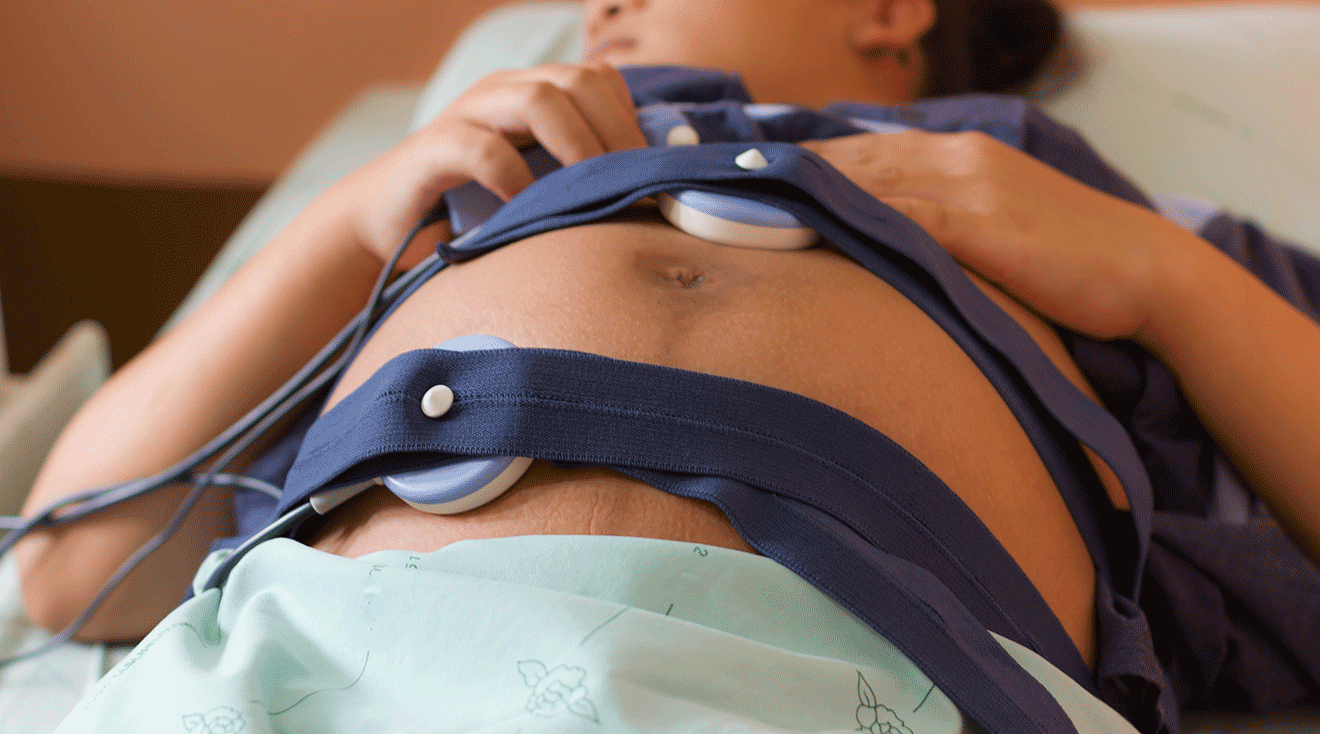
Once Cervidil is in place, your doctor will monitor the progress of your labor, as well as how baby is doing, to determine when it should be removed, Chuang says.
It depends. “Given alone, it could cause labor for some women,” Chuang says, particularly if your Bishop score, which measures several cervical conditions, is favorable. But many others need a follow-up treatment like Pitocin or amniotomy, she says.
“Cervidil is often used as a first-step medication to help the cervix soften, thin out and begin to dilate,” Sassin explains. “While every person is different, Cervidil can help kickstart the labor process by initially preparing the cervix for labor and delivery.”
Cervidil vs. Pitocin
Pitocin is often given after the cervix has ripened to help start contractions, says Sassin. “Generally, oxytocin—brand name Pitocin—is given after the cervix is ripened to continue the labor process,” she says. For some patients, cervical-ripening medication isn’t necessary, Sassin says. “Pitocin medication is administered through an IV and is a synthetic form of the hormone oxytocin, which is made naturally by the body,” she says. “Pitocin medication can start or strengthen contractions.”
Cervidil and Cytotec are both medications that are used to soften the cervix during induction and both contain a hormone-like substance called prostaglandins, Sassin explains. “One of the biggest differences is the way they’re administered,” she says. “Cervidil is an insert that sits in the back of the vagina near the cervix, generally for 12 hours. It is attached to a retrieval string, so it can be easily removed by your provider.”
Cytotec, which is a brand name for misoprostol, comes in a tablet form that can either be taken by mouth or placed in the vagina, Sassin says. It can be given every two to six hours as needed.
You’ll generally feel soft cramps and mild contractions when Cervidil starts working, Chuang says. Still, Sassin adds that “everyone is different.”
Most patients tolerate Cervidil well, Sassin says. But one side effect to watch for is a condition called uterine tachysystole, which is when contractions happen faster than normal. This can sometimes cause baby’s heart rate to become abnormal, she says. “Your provider will monitor you, your contraction pattern and your baby’s heart rate closely while the Cervidil is in place,” she adds.
Expectant parents could also have fever, chills or gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting or diarrhea, Sassin says.
Cervidil isn’t for everyone. “Cervidil isn’t recommended for patients with a known allergy or hypersensitivity to prostaglandin medications, who have contraindications to labor and vaginal birth, or who have had unexplained vaginal bleeding in pregnancy,” Sassin says. It’s also not meant for those who’ve had a c-section or uterine surgery, given the risk of complications.
Cervidil is a common medication used to help soften the cervix and induce labor. If you think it might be the right choice for you, or you have any questions about using it, reach out to your provider. They should be able to help answer your questions and concerns, and offer personalized guidance.
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
Plus, more from The Bump:
Meleen Chuang, MD, is a clinical associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine and medical director at the NYU Langone Family Health Center. She earned her medical degree from Stony Brook University School of Medicine in Stony Brook, New York.
Alexa Sassin, MD, is an assistant professor in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, where she also received her medical degree.
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Acute Tocolysis for Uterine Tachysystole or Suspected Fetal Distress, July 2018
Cervidil.com, Important Safety Information
Learn how we ensure the accuracy of our content through our editorial and medical review process.
Navigate forward to interact with the calendar and select a date. Press the question mark key to get the keyboard shortcuts for changing dates.